What is PROFIBUS?
PROFIBUS is a long-established fieldbus for connecting sensors and actuators with a central controller. It has proven to be a reliable and safe network technology. As a market-leading, standardised system, it enables the joint operation of automation and visualisation systems without a need for special interfaces. PROFIBUS is suitable both for smaller applications where time is critical and for highly complex communication tasks.
In order to ensure the stable functioning of any machine or system in the long term, the condition of all parts that are subject to wear needs to be monitored. Besides mechanical parts, this also includes the entire communication network with all its components.

Permanent PROFIBUS Network Monitoring
In the very near future, the challenges inherent to an increasingly higher degree of automation in production processes will be manageable only with a system solution for permanent network monitoring with the design goal of sending a warning before a failure occurs. Continuous monitoring of the fieldbus provides information about the current and past condition of a system to make maintenance plannable. This in turn ensures uninterrupted production without serious losses.
Passive data logger
The passive data logger checks PROFIBUS for typical quality parameters like error and repetitive telegrams, device diagnostics and device failures. These events are detected and stored in the device by means of preset trigger functions. The collected network data can be accessed via an integrated web interface for condition-based maintenance. A topology map stored in the device allows for the location of recorded events to be pinpointed to a specific segment and device.
Network monitoring software
A central network monitoring application aggregates the information of the distributed data logger in one location. This allows operators and maintainers of machines and systems to obtain all necessary information about the network condition at any time and receive warnings in case of anomalies.

PROFIBUS Maintenance and troubleshooting
When the permanent network monitoring system detects a deterioration in the condition of the PROFIBUS, the collected information enables the error to be localised precisely and corrected during planned maintenance.
All parameters that are important for the transmission quality can be checked with special diagnostic tools and brought back into the acceptable range with targeted measures.
The most common cause for changes in fieldbus installations is planned or unplanned intervention during maintenance or assembly work, as well as slow wear of component electronics and PROFIBUS cabling.
Quality tester
The quality tester is a universal diagnostic tool for online evaluation of the physical and logical communication quality of the data exchange in PROFIBUS networks. It provides comprehensive functionality for a quick and easy inspection of the entire network and does not require in-depth understanding of the signal shape or PROFIBUS data transmission.

Cable tester
The cable tester is used to check if the cables in a PROFIBUS network are routed correctly. The device indicates the real cable length and detects cable and shielding discontinuities as well as wiring errors. Passing a cable test is the prerequisite for clean signal transmission in a PROFIBUS network.
The cable test is performed with the system turned off. It is easy to use and has an easy to read clear-text display.
The PROFIBUS Tester PB-QONE is a measuring and diagnostic tool that was developed especially for commissioning and factory acceptance tests, maintenance and service as well as troubleshooting in PROFIBUS networks. Its ease of use and clear and automated evaluation of measuring results allow to reliably evaluate the state of the physical and logical transmission quality in the network. Regardless of the applied PROFIBUS protocol, this universal tool is used for PROFIBUS DP and PROFIBUS PA networks.
Check out the article: How to troubleshoot PROFIBUS systems with the PROFIBUS Tester PB-Q ONE
Physical evaluation
With the PROFIBUS tester PB-QONE measuring the transmission levels of the slaves in operation can be physically evaluated and displayed by a measurement bar chart for each slave. Each bar is a representation of the bit shape that results from the evaluation of the edge steepness, differential voltage and the transient response of the signal for each device. This evaluation now also takes into account the 7V drivers of modern PROFIBUS devices.
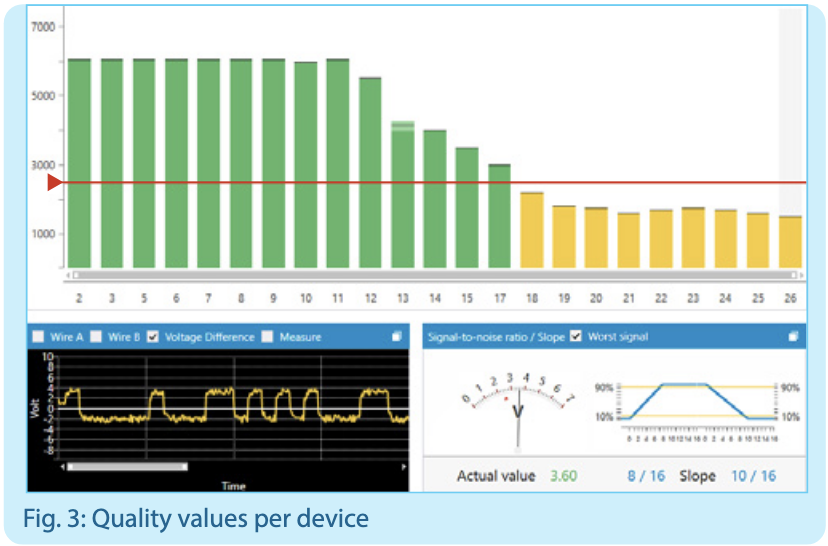
Logical evaluation
The analysis of the telegram traffic provides information about the communication quality of the network and indicates critical events including a clear text diagnosis of each device. Triggering for specific results is also possible to detect and analyse sporadic errors.
Topology scan
The entire bus topology is scanned in a fully automated and non-reactive manner during running production. The result of this scan is displayed directly and shows all segments of the master system, including repeaters, measuring points and cable lengths.

PROFtest II XL Cable Tester
The PROFtest II cable tester is used to check if the cables in a PROFIBUS network are routed correctly. The device indicates the real cable length and detects cable and shielding discontinuities as well as wiring errors. The cable test is done while the system is turned off and supports installers and maintainers with commissioning and service.
The test is performed in several steps, each from both ends of the segment. All results are stored on the device and can be printed out via a PC as a log.
Operating steps
- Test without termination
- Test with a switched bus termination (removed bus end)
- Test with both switched bus terminations at the segment ends
Testing criteria
The following tests are carried out when performing the individual operating steps:
- Display of actual cable length
- Cable impedance measurement
- Correct termination
- Cable discontinuity
- Shielding discontinuity
- Swapped cables A.B
- Cable short A-B
- Shielding short for cables A/B
- Use of improper cable types
- Determining reflections
The test is always done from both ends of the relevant segment (see next section, PROFIBUS measuring points).

Logging
All results of each step are stored on the device and can be printed out via a PC as a log.

PROFIBUS measuring points
Why measuring points in the PROFIBUS network?
Feedback-free measuring points to connect essential diagnostic tools are indispensable for communication analysis during commissioning, maintenance or troubleshooting.
A measuring point is a defined point of access to a system where the communication can be tested. This allows you to access the machines and systems at any time, even during running production.
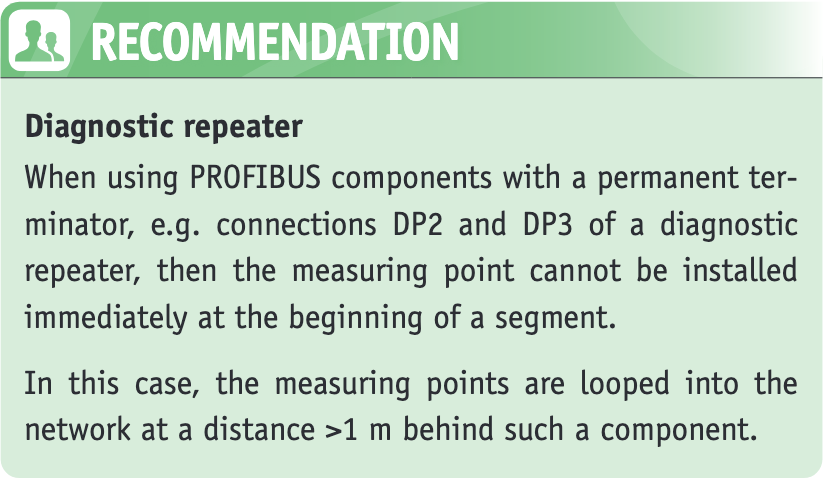
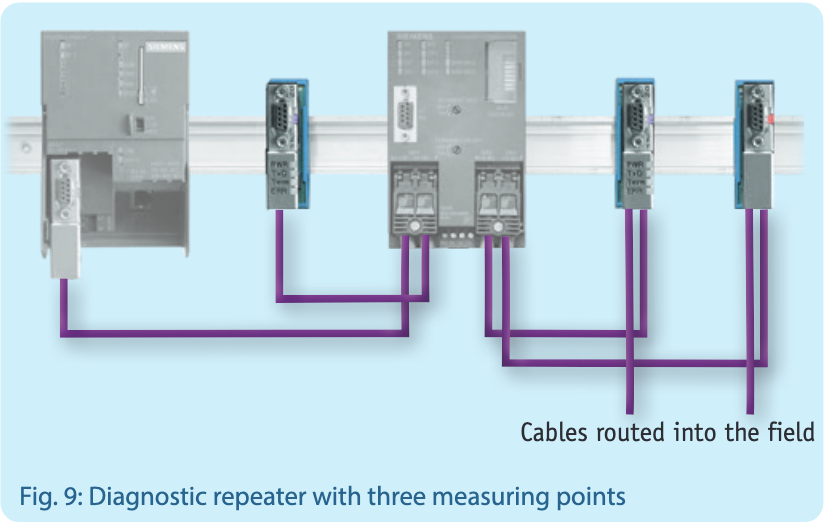
Diagnostic access should already be considered during the planning stage of a PROFIBUS network.

Practical example
It‘s a common assumption that one measurement per segment is sufficient to determine the transmission quality. However, practice shows that measurements at the beginning and the end of each segment are required. Faults in a segment may have varying effects. A measurement at the beginning of a segment may indicate trouble-free communication (see fig. 8) while the measurement at the end of the same segment shows a very different result (see fig. 10).
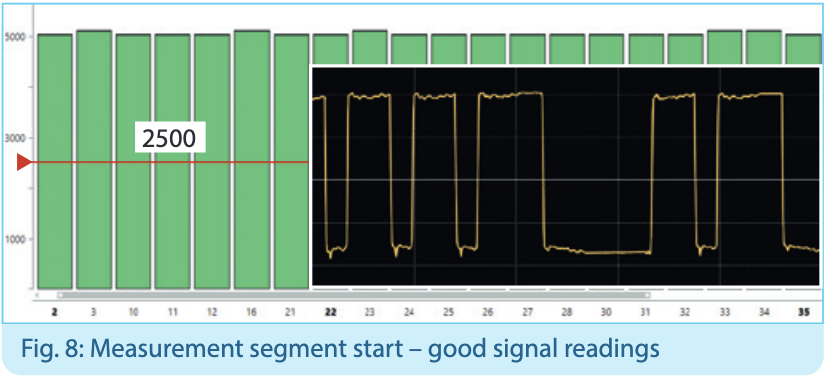

Because of such experiences, it is very important to conduct measurements at both ends of a segment.
Where should measuring points be installed?
A PROFIBUS network is fundamentally based on a linear structure. If required, it can be subdivided into separate, galvanically isolated segments by means of repeaters or other transducers. In each of these segments, several devices are connected that access the same medium for their communication.
This makes it necessary for all devices to understand each other. In order to also check the transmission quality, it is necessary to perform measurements both at the beginning and the end of a segment. Measuring points therefore need to be installed both at the beginning and the end of a segment.
A wide variety of PROFIBUS measuring points is available to cover all requirements. Depending on conditions and functionality, there is a choice between the following types of measuring point:
PROFIBUS DP
PROFIBUS PA
Keep learning:
PROFIBUS
Learn how to test and diagnose PROFIBUS systems in 5 stepsPROFINET
PROFINET in the context of Industry 4.0What is PROFINET?
PROFINET Network Planning
ServiceTool
How to use the Indu-Sol ServiceTool to identify the IP of PROFINET devicesPROFINET-INspektor®
How to configure ports in the PROFINET-INspektor®How to set PLC as Master in the PROFINET-INspektor®
How to set-up automatic topology scanning in the PROFINET-INspektor®
How to set-up automatic Switch scanning in the PROFINET-INspektor®
How to get reports and alarms from the web interface of the PROFINET-INspektor®
How to make a manual snapshot in the PROFINET-INspektor®





